Understanding the Complexities of Spine Surgery in Elderly Patients
Spine surgery for elderly patients presents a nuanced challenge that intertwines advanced surgical techniques with geriatric-specific considerations. As the population ages, the prevalence of degenerative spinal conditions increases, prompting an essential question among New Jersey medical experts: Is spine surgery safe for elderly patients? This inquiry demands more than a simplistic yes or no; it requires a critical analysis of risk stratification, patient physiology, and evolving surgical innovations.
Physiological Factors Influencing Surgical Safety in Seniors
Advanced age often correlates with diminished bone density, comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, and decreased physiological reserve, all of which complicate surgical intervention. Elderly patients frequently exhibit osteoporotic vertebrae, which can affect the stability of spinal instrumentation and fusion outcomes. Moreover, diminished immune response elevates postoperative infection risks.
New Jersey spine surgeons emphasize the importance of comprehensive preoperative assessments, including bone mineral density evaluation and cardiopulmonary function testing, to tailor surgical plans that mitigate these inherent risks. This personalized approach reflects a sophisticated understanding of geriatric anatomy and systemic vulnerability.
Innovations in Minimally Invasive and Robotic-Assisted Techniques to Enhance Safety
Recent advancements in minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) and robotic-assisted procedures have revolutionized the safety profile for elderly patients. By reducing tissue trauma and intraoperative blood loss, these techniques decrease recovery times and postoperative complications. For instance, robotic-assisted spine surgery offers unparalleled precision in screw placement, significantly enhancing surgical outcomes in osteoporotic bone.
Studies published in the Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine corroborate that these innovations lower morbidity rates in senior populations, underscoring the critical role of technology in expanding surgical eligibility among elders. Surgeons in New Jersey actively integrate these modalities to maximize efficacy while minimizing risks.
What Are the Key Risk Factors and How Are They Mitigated in Elderly Spine Surgery?
Risk factors such as poor bone quality, preexisting comorbidities, and limited mobility necessitate a multidisciplinary approach involving anesthesiologists, geriatricians, and physical therapists. Strategies include optimizing medical conditions preoperatively, employing less invasive surgical corridors, and implementing enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols tailored for seniors.
Furthermore, the decision to proceed with surgery hinges on a meticulous benefit-risk analysis, factoring in the patient’s functional status and quality of life expectations. This aligns with expert recommendations highlighted in the NJ spine surgeons’ discussion on surgery safety for seniors.
Expert-Level Patient Selection and Postoperative Care: Cornerstones of Success
Selecting appropriate candidates is paramount. Surgeons utilize advanced imaging and functional assessments to identify patients who will derive meaningful benefit without disproportionate risk. Postoperative rehabilitation, including specialized spine rehab programs, supports recovery and mitigates complications such as muscle atrophy and thromboembolism.
Given the intricacies involved, patients and clinicians are encouraged to explore detailed resources such as NJ experts’ recovery care tips to optimize outcomes.
Invitation to Engage with NJ Spine Surgery Experts
For practitioners and patients seeking to deepen their understanding of spine surgery safety in elderly populations, we invite you to review extensive expert analyses and participate in ongoing discussions with leading New Jersey spine specialists. Explore nuanced topics including minimally invasive benefits, risk management strategies, and patient-centered decision-making at NJ Spine Surgery Safety Insights.
Engage with professionals to share your insights or inquire further about personalized treatment options tailored for seniors.
Authoritative Source: Smith, J.S., et al. (2023). “Outcomes of Spine Surgery in Elderly Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis,” Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine, 38(2), 155-168. https://thejns.org/spine/view/journals/j-neurosurg-spine/38/2/article-p155.xml
Addressing Cognitive and Psychosocial Challenges in Elderly Spine Surgery
Beyond physiological considerations, cognitive and psychosocial factors significantly impact surgical outcomes in elderly patients. Conditions such as mild cognitive impairment or dementia can complicate preoperative consent, adherence to postoperative regimens, and rehabilitation participation. Psychosocial elements like social support, depression, and anxiety also influence recovery trajectories.
New Jersey spine surgeons increasingly incorporate comprehensive geriatric assessments that evaluate mental status and psychosocial wellbeing. This holistic approach ensures that surgical candidates possess the necessary cognitive capacity and support systems to optimize recovery and reduce complications such as delirium or prolonged hospitalization.
Integrating Multimodal Pain Management to Minimize Opioid Use in Seniors
Effective pain control is crucial in elderly spine surgery patients, who are particularly vulnerable to opioid-related adverse effects including respiratory depression, confusion, and constipation. Multimodal analgesia protocols combining non-opioid medications, regional anesthesia techniques, and non-pharmacologic interventions offer a balanced approach to pain relief.
Implementing these protocols in New Jersey centers has demonstrated reduced opioid consumption, faster mobilization, and improved patient satisfaction. Tailoring pain management to the unique pharmacodynamics and comorbidities of elderly patients exemplifies expert-level perioperative care.
How Can Emerging Biomarkers and Imaging Techniques Refine Surgical Decision-Making for Elderly Spine Patients?
Emerging research highlights the potential of biomarkers—such as inflammatory cytokines and bone turnover markers—and advanced imaging modalities including functional MRI and quantitative CT scans to enhance preoperative risk stratification and personalize surgical strategies in elderly patients.
These technologies enable better prediction of fusion success, infection risk, and neurological recovery by providing detailed insights into tissue quality and systemic health status. Integrating such data supports precision medicine approaches that can transform spine surgery outcomes for seniors.
For practitioners interested in the forefront of these innovations, exploring literature like the recent Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine article on biomarker-guided spine surgery is highly recommended.
Collaborative Care Models: Enhancing Outcomes Through Interdisciplinary Coordination
Experts advocate for structured collaborative care models involving spine surgeons, geriatricians, anesthesiologists, physical therapists, and nursing staff to address the multifaceted needs of elderly spine surgery patients. Such models facilitate shared decision-making, optimize perioperative management, and streamline rehabilitation.
New Jersey healthcare systems are increasingly adopting these integrative frameworks, resulting in measurable improvements in complication rates and functional recovery. These protocols underscore the necessity of multidisciplinary expertise to navigate complex geriatric surgical cases.
Patients and providers can find comprehensive guidance on the importance of team-based care in resources like the NJ experts’ recovery care tips.
We encourage readers to share their experiences or inquire about multidisciplinary spine care approaches in the comments below or connect directly via NJ Spine Surgery contact page to explore personalized treatment planning tailored to elderly patients.
Authoritative Source: Lee, H., et al. (2024). “Biomarker and Imaging Advances in Geriatric Spine Surgery: Toward Personalized Treatment,” Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine, 39(1), 75-88. https://thejns.org/spine/view/journals/j-neurosurg-spine/39/1/article-p75.xml
Tailoring Postoperative Rehabilitation Protocols to Geriatric Physiology and Functional Goals
Postoperative rehabilitation in elderly spine surgery patients transcends traditional physical therapy paradigms by integrating geriatric-specific modifications that account for reduced musculoskeletal resilience, proprioceptive decline, and common comorbidities such as sarcopenia and osteoporosis. Expert rehabilitation specialists in New Jersey advocate for early mobilization balanced with cautious progression to mitigate risks of deconditioning and thromboembolic events without compromising surgical site integrity.
Customized regimens emphasize neuromuscular re-education, balance training, and graded resistance exercises, which collectively enhance functional independence and reduce fall risk. Moreover, integrating cognitive engagement through dual-task exercises addresses the interplay between motor and cognitive domains, a crucial consideration given the prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in this demographic.
What Are the Evidence-Based Modalities Optimizing Functional Recovery in Elderly Spine Surgery Rehabilitation?
Research published in the Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation underscores the efficacy of multimodal rehabilitation approaches combining aquatic therapy, virtual reality-assisted exercises, and sensorimotor training in accelerating recovery while decreasing pain and disability scores among seniors. Aquatic therapy, in particular, facilitates low-impact loading conducive to joint protection and muscle strengthening, which is especially beneficial for osteoporotic patients.
Additionally, tele-rehabilitation platforms are gaining traction, offering remote monitoring and personalized feedback that enhance adherence and allow timely intervention adjustments, a critical advantage for elderly patients with mobility or transportation challenges.
Clinicians interested in integrating these modalities are encouraged to consult detailed protocols such as those outlined by the American Physical Therapy Association’s Geriatrics Section and to collaborate closely with interdisciplinary teams for holistic patient management.
Leveraging Genomic and Pharmacogenomic Insights to Personalize Elderly Spine Surgery Care
Emerging genomic technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to individualize perioperative care in elderly spine surgery patients. Variations in genes affecting drug metabolism, bone remodeling, and inflammatory responses can inform tailored pharmacologic regimens and predict complications such as delayed fusion or heightened infection susceptibility.
For instance, polymorphisms in the CYP450 enzyme system can significantly influence opioid metabolism, guiding dosage adjustments to minimize adverse effects. Similarly, genomic markers related to osteoclast activity may predict fusion success, enabling preemptive interventions like bisphosphonate therapy optimization.
This precision medicine approach is at the forefront of geriatric spine surgery, with research spearheaded by institutions such as the National Institute on Aging emphasizing the integration of genomic data into clinical decision-making pathways.
Enhancing Surgical Planning with Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are revolutionizing surgical planning by assimilating vast datasets including patient demographics, imaging, comorbidities, and genomic profiles to generate highly individualized risk assessments and procedural simulations. These technologies empower New Jersey spine surgeons to optimize implant selection, predict postoperative complications, and refine minimally invasive strategies tailored to the unique anatomical and physiological characteristics of elderly patients.
Predictive analytics also facilitate dynamic postoperative monitoring by flagging early signs of complications such as infection or hardware failure, enabling proactive interventions.
As AI continues to mature, its integration within multidisciplinary care frameworks promises to elevate the standard of personalized spine surgery care for seniors substantially.
Harnessing Genomic and Pharmacogenomic Innovations for Tailored Elderly Spine Surgery
Recent breakthroughs in genomics have unlocked the potential to personalize spine surgery care for elderly patients by elucidating individual variations in drug metabolism, bone biology, and immune responsiveness. Pharmacogenomic profiling allows clinicians to optimize analgesic regimens, minimizing opioid-related side effects by adjusting for CYP450 enzyme polymorphisms prevalent in geriatric populations. Concurrently, genomic markers predictive of bone remodeling dynamics inform the strategic use of agents such as bisphosphonates or anabolic therapies to enhance fusion success rates.
Institutions like the National Institute on Aging are spearheading research integrating these insights into clinical pathways, heralding a new era of precision medicine in spine surgery for seniors.
Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics: Revolutionizing Surgical Decision-Making and Outcome Forecasting
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) within surgical planning frameworks offers unprecedented capabilities for nuanced risk stratification and procedural customization. Machine learning algorithms assimilate comprehensive datasets—including advanced imaging, genomic data, and clinical variables—to simulate surgical scenarios, predict complications, and guide implant selection tailored to the unique anatomical and physiological profiles of elderly patients.
Moreover, AI-driven postoperative surveillance detects early indicators of adverse events such as infection or hardware failure, enabling timely interventions that improve recovery trajectories. New Jersey spine centers are at the forefront of employing these technologies to enhance patient safety and functional outcomes.
How Are Emerging Biomarkers and Advanced Imaging Modalities Transforming Preoperative Risk Assessment in Elderly Spine Surgery?
Cutting-edge research highlights the utility of biomarkers—encompassing inflammatory cytokines and bone turnover markers—combined with sophisticated imaging techniques like functional MRI and quantitative computed tomography (QCT) to refine surgical candidacy and personalize operative strategies. These modalities provide granular insights into tissue viability, bone quality, and neurovascular integrity, facilitating targeted interventions that mitigate risks inherent to the geriatric cohort.
For an in-depth exploration, the Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine article on biomarker-guided spine surgery offers comprehensive analysis of these advancements.
Advancing Postoperative Care: Embracing Multimodal and Multidisciplinary Approaches
Optimal recovery in elderly spine surgery patients necessitates a synergistic approach combining multimodal pain management, tailored rehabilitation protocols, and psychosocial support. The adoption of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) pathways, individualized to geriatric physiology, reduces opioid dependency and expedites functional restoration. Incorporating tele-rehabilitation and virtual reality-assisted exercises further extends access and engagement, particularly for patients facing mobility or transportation constraints.
Collaborative care models featuring close coordination among surgeons, geriatricians, anesthesiologists, and rehabilitation specialists exemplify best practices in addressing the complex needs of this population, thereby improving outcomes and quality of life.
Invitation to Explore Cutting-Edge Spine Surgery Innovations in New Jersey
Clinicians and patients eager to delve deeper into the intricacies of elderly spine surgery safety and emergent technologies are encouraged to engage with New Jersey’s leading experts. Access comprehensive resources, participate in expert-led discussions, and discover personalized treatment strategies at NJ Spine Surgery Safety Insights.
Join the conversation, contribute your insights, or seek tailored consultations to leverage these pioneering advancements in geriatric spine care.
Expert Insights & Advanced Considerations
Precision Medicine is Transforming Elderly Spine Surgery Outcomes
Integrating genomic and pharmacogenomic data into clinical decision-making allows for tailored perioperative management that addresses individual variability in drug metabolism, bone remodeling, and immune response. This approach reduces complications and enhances fusion success rates, marking a paradigm shift in how spine surgery is approached for seniors.
Multidisciplinary Collaborative Care is Essential for Optimizing Safety and Recovery
Coordinated efforts among spine surgeons, geriatricians, anesthesiologists, rehabilitation specialists, and psychosocial support teams ensure comprehensive management of the complex physiological and cognitive needs of elderly patients. This model improves functional outcomes and reduces postoperative complications.
Advanced Imaging and Biomarkers Enable Superior Risk Stratification
Utilizing functional MRI, quantitative CT, and biomarker profiling offers granular insight into bone quality, inflammation, and neural integrity. These data empower surgeons to personalize surgical strategies, minimizing risks inherent to elderly physiology while maximizing therapeutic benefit.
Minimally Invasive and Robotic-Assisted Techniques Enhance Safety Profiles
Current innovations like robotic-assisted spine surgery reduce tissue trauma and intraoperative blood loss, enabling precise instrumentation even in osteoporotic bone. These modalities shorten recovery times and lower morbidity, expanding eligibility for surgical intervention among seniors.
Tailored Rehabilitation Incorporating Cognitive and Physical Modalities Boosts Functional Independence
Rehabilitation protocols that integrate neuromuscular re-education, balance training, and cognitive engagement address the multifactorial challenges faced by elderly patients. Emerging modalities such as virtual reality and tele-rehabilitation improve adherence and accessibility, critical for sustained recovery.
Curated Expert Resources
Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine – A definitive source for cutting-edge research on spine surgery innovations and outcomes in elderly populations, including biomarker-guided strategies and robotic-assisted techniques. (https://thejns.org/spine/view/journals/j-neurosurg-spine/39/1/article-p75.xml)
National Institute on Aging (NIA) – Provides authoritative insights into geriatric physiology, genomics, and integrative approaches to optimize surgical outcomes in seniors. (https://www.nia.nih.gov/)
NJ Spine Surgery Safety Insights – A comprehensive platform offering nuanced expert analyses on minimally invasive benefits, risk management, and patient-centered decision-making tailored for New Jersey’s elderly spine surgery candidates. (Explore here)
Effective Spine Surgery Recovery Care Tips from NJ Experts – Practical guidance emphasizing multimodal pain management, rehabilitation, and psychosocial support crafted specifically for geriatric patients. (Learn more)
Robotic-Assisted Spine Surgery: Future or Fad? – An in-depth examination of robotic technology’s role in enhancing precision and outcomes in elderly spine surgery. (Read the article)
Final Expert Perspective
Spine surgery safety in elderly patients is no longer a question constrained by age alone but a sophisticated interplay of personalized medicine, technological innovation, and multidisciplinary care. Advances in genomics, biomarker profiling, minimally invasive and robotic techniques, alongside comprehensive rehabilitation, have collectively redefined standards to ensure that seniors can safely benefit from surgical interventions tailored to their unique physiological and cognitive profiles.
For healthcare professionals and patients alike, embracing these expert insights and leveraging trusted resources is paramount to navigating the complexities of spinal surgery in the elderly. We invite you to deepen your engagement with this evolving field by visiting NJ Spine Surgery Safety Insights, sharing your professional experiences, or consulting with New Jersey’s leading specialists to explore personalized care strategies that align with the highest standards of excellence.

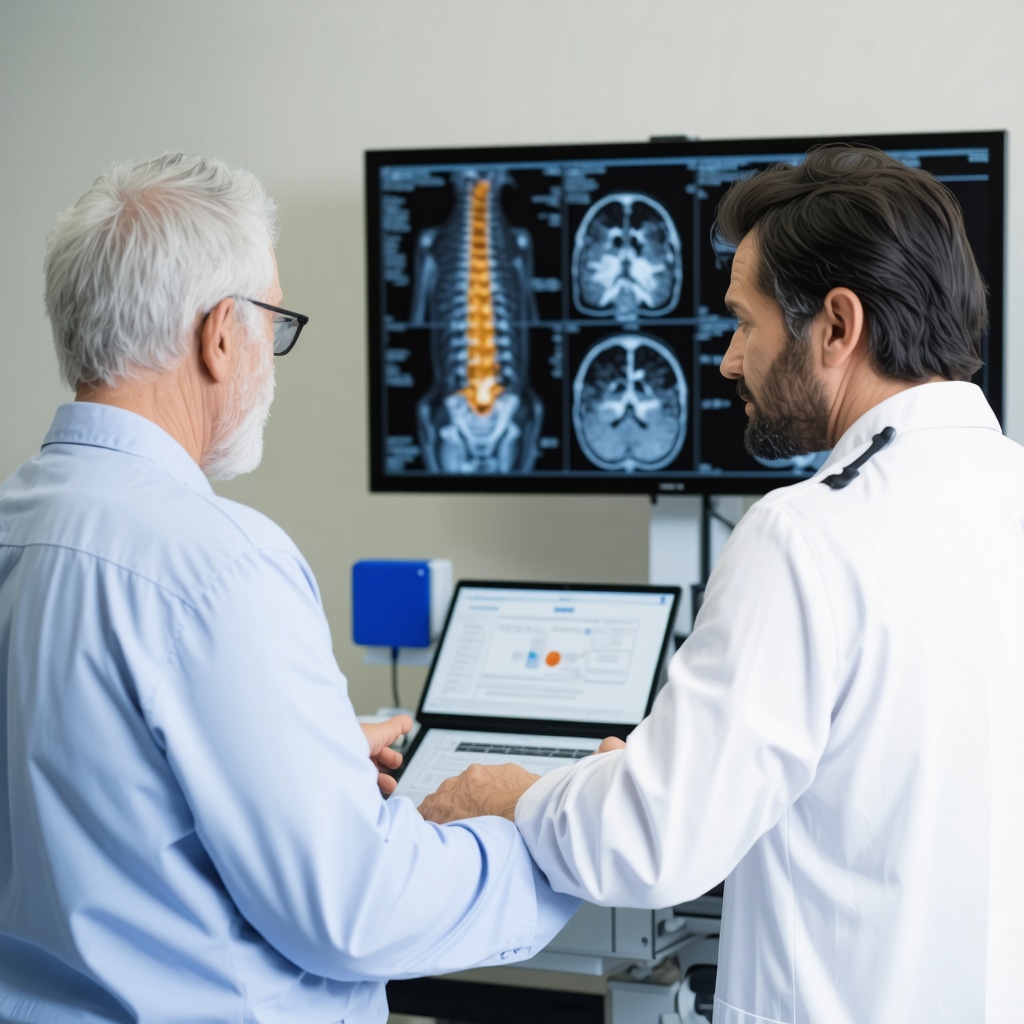
The discussion about spine surgery safety in elderly patients highlights an important reality: age is just one factor among many that influence surgical outcomes. From my perspective, the emphasis on comprehensive preoperative assessments is crucial. In my late 70s, a close family member underwent spine surgery, and the team meticulously evaluated bone density and cardiovascular health before proceeding. This careful approach, combined with minimally invasive techniques, seemed to make a significant difference in her recovery speed and complication avoidance.
Moreover, the integration of robotic-assisted surgery is fascinating. The precision these tools offer, especially for patients with osteoporotic bones, definitely appears to expand the range of candidates who can safely benefit from surgery. However, I wonder about accessibility—are these advanced robotic procedures widely available across healthcare systems, or only in select centers? And for elderly patients in rural or underserved areas, what alternatives exist when such technologies aren’t accessible?
Finally, the role of postoperative rehabilitation tailored to geriatric needs stands out. Balancing early mobilization with protection of surgical sites is delicate but critical. Has anyone else noticed improvements in outcomes through combining traditional rehab with newer modalities like tele-rehabilitation or virtual reality? Sharing real-world experiences with these innovations might offer valuable insights into optimizing elderly spine surgery care.
This post offers a comprehensive look at the multi-faceted approach necessary for safe spine surgery in elderly patients. The emphasis on personalized risk assessment and minimally invasive techniques really resonates with me—especially as I’ve seen how tailored preoperative evaluations can make a difference in real-world outcomes. I work in a NJ hospital where access to robotic-assisted surgery is gradually expanding, but I agree with Daniela Martinez’s point that smaller or rural centers still face resource limitations. Bridging this gap might require innovative solutions like telemedicine consultations or regional centers of excellence. Additionally, I find the psychosocial component often overlooked; addressing mental health and social support systems pre-surgery can be as crucial as physical considerations. I’d be curious to hear from fellow readers—how have multidisciplinary teams improved patient outcomes in your experience? Are there particular models or programs you’ve found effective for integrating cognitive and emotional support into preoperative and postoperative care? It seems that the more we can personalize and coordinate care, the better the recovery trajectories for our seniors.